Automotive Engine Technologies
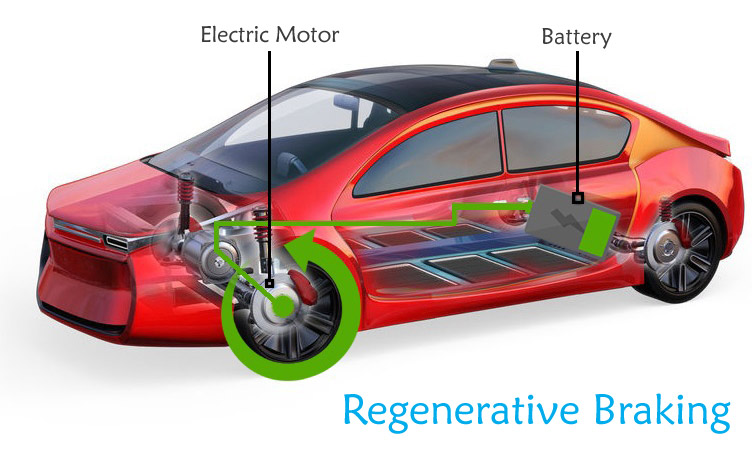
Electric Regen braking :
"Regenerative braking systems (RBSs) are a type of kinetic energy recovery system that transfers the kinetic energy of an object in motion into potential or stored energy to slow the vehicle down, and as a result increases fuel efficiency.[2] These systems are also called kinetic energy recovery systems. There are multiple methods of energy conversion in RBSs including spring, flywheel, electromagnetic and hydraulic. More recently, an electromagnetic-flywheel hybrid RBS has emerged as well. Each type of RBS utilizes a different energy conversion or storage method, giving varying efficiency and applications for each type.
RBSs are installed along the drive train or fitted to the drive wheels of a vehicle where they inhibit the motion of the wheels using magnetic fields or mechanical torque. These methods of motion inhibition allow energy to be generated under braking, as opposed to friction brakes which simply waste away energy to slow the vehicle by turning the kinetic energy into thermal energy. "
After completion the demo of AUTOMOTIVES, the students will have an practical session on both automotive technology and RBS.
Engine :
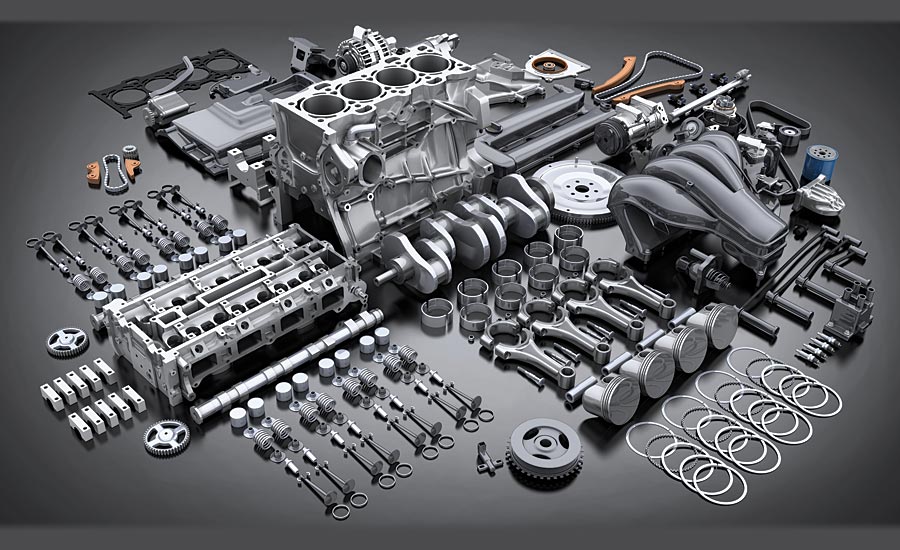
The term internal combustion engine usually refers to an engine in which combustion is intermittent, such as the more familiar four-stroke and two stroke piston engines, along with variants, such as the six-stroke piston engine and the Wankel rotary engine. A second class of internal combustion engines use continuous combustion: gas turbines, jet engines and most rocket engines, each of which are internal combustion engines on the same principle as previously described. Firearms are also a form of internal combustion engine .In contrast, in external combustion engines, such as steam or Sterling engines, energy is delivered to a working fluid not consisting of, mixed with, or contaminated by combustion products. Working fluids can be air, hot water, pressurized water or even liquid sodium, heated in a boiler. ICEs are usually powered by energy-dense fuels such as gasoline or diesel, liquids derived from fossil fuels. While there are many stationary applications, most ICES are used in mobile applications and are the dominant power supply for vehicles such as cars, aircraft, and boats. Typically an ICE is fed with fossil fuels like natural gas or petroleum products such as gasoline, diesel fuel or fuel oil. There is a growing usage of renewable fuels like biodiesel for compression ignition engines and bioethanol or methanol for spark ignition engines. Hydrogen is sometimes used, and can be made from either fossil fuels or renewable energy.
AGENDA FOR WORKSHOP
- #Basics
- #Dismantling and assembling of IC engines Hands on session
- This is going to be a wonderful learning experience
- This is 2 days Workshop
- Certificate of participation will be provided to all the participated candidates.
- Registration fee: Rs 900/-per person.
- Combo of automotive+Nino robot : Rs 1200 for each person
- Engine Assembly & Disassembly
- 4 Stroke 4 Cylinder Desiel Engine
- 4 Stroke 3 Cylinder Petrol Engine
- Automotive Suspension Analysis
- Regenerative Braking System Proto Type
- For participants who are interested to participate in multiple events, surprise discount will be provided at registration desk.